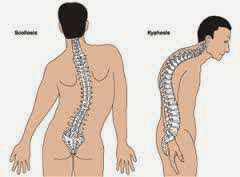
Three forms of structural scoliosis are:
- Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common form and classified into 3 groups: infantile, which arise from birth to age 3 years; children, who emerged from the age of 3 years to 10 years; and adolescents, which appears after the age of 10 years (the age of the most common).
- Congenital scoliosis is scoliosis that causes malformation of one or more vertebral bodies.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis, children who suffer from neuromuscular diseases (such as brain paralysis, spina bifida, or muscular dystrophy) which directly causes the deformity.
Clinical Symptoms
- Spine curves abnormally to the side.
- Shoulder or hip and the left and right are not the same height.
- Back pain.
- Fatigue in the spine after sitting or standing for long.
- Severe scoliosis (curvature greater than 60) can cause respiratory problems.
Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Scoliosis
1. Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to emphasis the lung.
Goal: effective breathing pattern.
Intervention:
- Assess respiratory status every 4 hours.
- Help and teach the patient to do deep breaths every 1 hour.
- Set the semi-Fowler position bed to improve lung expansion.
- Auscultation of the chest to listen for breath sounds every 2 hours.
- Monitor vital signs every 4 hours.
2. Acute pain: back related to body position tilted laterally.
Goal: pain is reduced / lost.
Intervention:
- Assess the type, intensity, and location of pain.
- Adjust the position of which can increase the sense of comfort.
- Maintain a quiet environment to improve comfort.
- Teach relaxation and distraction techniques to divert attention, thus reducing pain.
- Encourage regular postural exercises to improve posture.
- Teach and encourage use of the brace to reduce pain during activity.
- Collaboration in providing analgesic to relieve pain.
3. Impaired physical mobility related to an unbalanced posture.
Objective: To improve physical mobility.
Intervention:
- Assess the level of physical mobility.
- Increase activity if pain is reduced.
- Teaching aids and active joint range of motion exercises.
- Involve the family in performing self-care.
- Increase return to normal activity.
4. Disturbed Body Image or Self-concept disturbance related to kelateral tilted posture.
Objective: To enhance the image of the body.
Intervention:
- Instruct to express feelings and problems.
- Give supportive environment.
- Help the patient to identify positive coping styles.
- Give realistic expectations and goals for the short term to facilitate the achievement.
- Give rewards for tasks performed.
- Encourage communication with people nearby and need socialization with family and friends.
- Give encouragement to care for themselves as tolerated.
5. Knowledge Deficit related to lack of information about the disease.
Goal: understanding of the treatment program.
Intervention:
- Explain about the state of the disease.
- Emphasize the importance and benefits of maintaining the recommended exercise program.
- Tell us about the treatment of: name, schedule, purpose, dosage, and side effects.
- Demonstrate the installation and maintenance brace or corset.